Fire
Fires start when a flammable or a combustible material, in
combination with a sufficient quantity of an oxidizer such as oxygen gas or
another oxygen-rich compound (though non-oxygen oxidizers exist), is exposed to
a source of heat or ambient temperature above the flash point for the
fuel/oxidizer mix, and is able to sustain a rate of rapid oxidation that
produces a chain reaction. This is commonly called the fire tetrahedron. Fire
cannot exist without all of these elements in place and in the right
proportions. For example, a flammable liquid will start burning only if the
fuel and oxygen are in the right proportions. Some fuel-oxygen mixes may
require a catalyst, a substance that is not consumed, when added, in any
chemical reaction during combustion, but which enables the reactants to combust
more readily.
Once ignited, a chain reaction must take place whereby fires
can sustain their own heat by the further release of heat energy in the process
of combustion and may propagate, provided there is a continuous supply of an
oxidizer and fuel.
General
Fire Fighting Equipment
Fire fighting systems and equipment vary depending on the
age, size, use and type of building construction. A building may contain some
or all of the following features:
Fire extinguishers
Fire hose reels
Fire hydrant systems
Automatic sprinkler systems.
Fire extinguishers
Fire extinguishers are provided for a 'first attack' fire
fighting measure, generally undertaken by the occupants of the building before
the fire service arrives. It is important that occupants are familiar with
which extinguisher type to use on which fire.
Most fires start as a small fire and may be extinguished if
the correct type and amount of extinguishing agent is applied whilst the fire
is small and controllable.
The principle fire extinguisher types currently available
include:
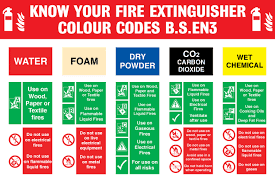
Extinguishing
Agent Principle Use
- Water - Wood and paper fires - not electrical
- Foam - Flammable liquid fires - not electrical
- Carbon dioxide - Electrical fires
- Dry chemical - Flammable liquids and electrical fires
- Wet chemical - Fat fires - not electrical
- K Type- Cooking Oils.
Firefighter
duties
A firefighter's goals are to save lives, property, and the
environment. A fire can rapidly spread and endanger many lives, but with modern
firefighting techniques, catastrophe can often be avoided. To prevent fires
from starting, a firefighter's duties may include public education about fire
safety and conducting fire inspections of locations to verify their adherence
to local fire codes.
Firefighter
skills
A firefighter doing a ladder slide, which is used to quickly
escape from a window Firefighting requires skills in fire suppression, rescue,
and hazardous materials mitigation. Firefighters must also have, or be able to
acquire, knowledge of department organizations, operations, and procedures and
the district or city street system. They will have to negotiate in order to
perform their duties.
They must meet minimum physical fitness standards and learn
various firefighting duties within a reasonable period.
Examples are:
- ·
Building construction
- ·
Fire dynamics
- ·
Firefighting PPE
- ·
Fire extinguishers
- ·
Ropes and knots
- ·
Ground ladders
- ·
Forcible entry
- ·
Structural search and rescue
- ·
Tactical ventilation
- ·
Fire hose operations and streams
- ·
Fire suppression
- ·
Overhaul, property conservation, and scene
preservation
- ·
Building materials, structural collapse, and effects
of fire suppression
- ·
Technical rescue support and vehicle extrication
operations
- ·
Foam fire fighting, liquid fires, and gas fires
- ·
Hazardous materials response
Specialized
skills
Specialized areas of operations may require subject-specific
training.
A hose team training to fight an aircraft fire aboard a US
aircraft carrier, 2006
Examples are:
- · Fire apparatus driver/operator - trained to drive fire apparatus to and from fires and other emergencies, operate fire-apparatus pumps and aerial devices, and maintains apparatus.
- ·
Hazardous materials technician - certified to mitigate
hazardous materials and CBRNE emergencies.
- ·
Rescue Technician - certified to perform rescues such
as high-angle rope, trench, structural collapse, confined space, vehicle and
machinery, water, ice, and cave or mine rescues.
- ·
Airport Firefighter - trained in ARFF.
- ·
Wildland Firefighter - trained to extinguish fires in
outdoor vegetation, including the wildland/urban interface.
A self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), sometimes referred to as a compressed air breathing apparatus (CABA) or simply breathing apparatus (BA), is a device worn by rescue workers, firefighters, and others to provide breathable air in an immediately dangerous to life or health atmosphere (IDLH). When not used underwater, they are sometimes called industrial breathing sets. The term self-contained means that the breathing set is not dependent on a remote supply. If designed for use under water, it is called SCUBA. (Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus).
Personal
protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing,
helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the
wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective
equipment include physical, electrical, heat, chemicals, biohazards, and
airborne particulate matter. Protective equipment may be worn for job-related
occupational safety and health purposes, as well as for sports and other
recreational activities. "Protective clothing" is applied to traditional
categories of clothing, and "protective gear" applies to items such
as pads, guards, shields, or masks, and others.
The purpose of personal protective equipment is to reduce
employee exposure to hazards when engineering controls and administrative
controls are not feasible or effective to reduce these risks to acceptable
levels. PPE is needed when there are hazards present. PPE has the serious
limitation that it does not eliminate the hazard at the source and may result
in employees being exposed to the hazard if the equipment fails.




No comments:
Post a Comment